Mazdutide peptide is an innovative dual-target peptide drug that acts as an agonist for both the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor and the glucagon (GCGR) receptor. This unique dual-action mechanism gives it significant advantages in the treatment of metabolic diseases, enabling it to regulate blood sugar levels and promote energy metabolism simultaneously. The molecular structure of Mazdutide has been meticulously designed, with a 40-amino-acid sequence ingeniously balancing the activation effects of both receptors, retaining the hypoglycemic properties of traditional GLP-1 analogues while adding additional metabolic benefits from the GCGR pathway. Clinical studies have shown that Mazdutide not only effectively improves blood sugar control in patients with type 2 diabetes but also significantly reduces weight, improves lipid profiles, and alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Its innovative long-acting formulation technology enables a once-weekly or bi-weekly dosing regimen, significantly enhancing patient compliance. As a new generation of metabolic regulators, Mazdutide represents a significant breakthrough in peptide drug research and development, providing a new option for the comprehensive management of complex metabolic disorders.
|
|
|



Mazdutide Powder COA


Mazdutide peptide (also known as IBI362 or LY3305677) is an innovative dual receptor agonist drug. Its discovery process can be traced back to in-depth research on mammalian gastric acid regulatory hormone (Oxyntomodulin, OXM). OXM, as a naturally occurring gastrointestinal hormone, is secreted by intestinal L cells and has the dual functions of activating glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) and glucagon receptor (GCGR). This characteristic makes it play a crucial role in regulating energy balance, glucose metabolism, and weight control. Early studies have shown that exogenous administration of OXM can improve glucose tolerance and promote weight loss, but its natural peptide has a short half-life and requires frequent administration, limiting its clinical application potential.
To overcome this limitation, scientists have been working on developing long-acting OXM analogues. The development of Mazdutide is based on this goal, by modifying its structure to extend its duration of action. Specifically, researchers introduced fatty acyl side chains into the OXM molecule to form a long-acting synthetic peptide. This modification strategy significantly prolonged the drug's half-life, enabling a once-weekly administration frequency and greatly enhancing patient compliance. In the early 2020s, the early research data of Mazdutide gradually became public, revealing its unique mechanism as a dual agonist of GLP-1R/GCGR. Compared with single receptor agonists, Mazdutide activates both receptors simultaneously, not only enhancing weight loss and hypoglycemic effects, but also avoiding the side effect of elevated blood sugar caused by excessive stimulation of the glucagon receptor through balancing receptor activation.
 |
 |
 |
The clinical research of Mazdutide began around 2021. The initial trials mainly focused on safety and the assessment of initial efficacy. A 1b phase multi-dose escalating study (NCT04466904) targeting Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes showed that after 12 weeks of treatment with Mazdutide, the patients' glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels significantly decreased, with a range of -1.46% to -2.23%, and the weight reduction could reach 5.4%. These data not only verified the dual mechanism of Mazdutide but also laid the foundation for its further development in the field of metabolic diseases.
Subsequently, the clinical research of Mazdutide expanded to include obese and overweight populations. In a 1b phase randomized controlled trial published in 2022, Chinese adult obese patients who received Mazdutide treatment for 12 weeks experienced a maximum weight reduction of up to 6.4%, and the drug was well tolerated. The safety profile was similar to that of other GLP-1 receptor agonists. This result further supported the potential of Mazdutide as a weight loss drug. In 2025, the development of Mazdutide achieved a milestone breakthrough. The National Medical Products Administration of China (NMPA) officially approved its use for the chronic weight management of Chinese adult obese or overweight patients, making it the first GLP-1 receptor agonist dual GCG/GLP-1 receptor agonist to be approved for weight loss worldwide.
In the same year, the results of the pivotal 3rd phase clinical study of Mazdutide (GLORY-1) were published in the New England Journal of Medicine. The study showed that after 20 weeks of treatment, the weight reduction of patients in the Mazdutide group was significantly greater than that of the placebo group, reaching up to 5.7%, while the HbA1c level decreased by 1.70%. Moreover, Mazdutide demonstrated multi-dimensional metabolic benefits, including reduced waist circumference, improved blood lipids and blood pressure, decreased serum uric acid and liver enzyme levels, reduced liver fat content, and enhanced insulin sensitivity. These comprehensive benefits made Mazdutide stand out in the field of metabolic disease treatment.
The approval and launch of Mazdutide marks a significant breakthrough in China's research and development of drugs for endocrine and metabolic diseases. Its innovative dual-receptor agonist mechanism provides a new strategy for the treatment of obesity and related metabolic disorders. As the world's first approved drug of its kind, Mazdutide not only fills the market gap but also redefines the standards for the treatment of metabolic diseases through its outstanding clinical data. With its widespread application in clinical practice, Mazdutide is expected to offer better treatment options for hundreds of millions of obese and overweight patients worldwide, while also promoting the research and development of dual-receptor agonist drugs and opening a new chapter in the treatment of metabolic diseases.
From deep-sea biological toxins to the inspiration for therapeutic peptides
In the field of biomedicine, drawing inspiration from the complex biological molecules in nature and transforming them into therapeutic drugs is an innovative path full of challenges and opportunities. Mazdutide (Mazdutide peptide) is a new type of dual agonist for glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) and glucagon receptor (GCGR). Its development process is a vivid illustration of this innovative path. Particularly notable is that part of its design inspiration comes from in-depth research on the structures of deep-sea biological toxins. This cross-disciplinary exploration has opened up new horizons for the treatment of metabolic diseases.
Deep-sea biological toxins: The "chemical factory" of nature
The deep-sea environment, with its extreme pressure, low temperature, darkness and unique ecosystem, has given rise to numerous structurally complex and functionally diverse biological toxins. These toxins are not only key components of the defense mechanisms of marine organisms, but also a treasure trove of natural product chemistry. For instance, polyether toxins such as those from the rock sand anemone and Xijia, with their unique trapezoidal cyclic polyamide structures, exhibit extremely high toxicity, while peptide toxins like yurolin toxins exert biological activity through precise target recognition mechanisms. The common feature of these toxins is their highly complex structures and specific functions, providing rich molecular templates for drug development.
Although there are risks in directly using the toxicity of deep-sea toxins for drug development, the diversity of their chemical structures and the specificity of their biological activities provide important insights for drug design. Scientists analyze the molecular structure of the toxins, identify their key active sites, and use chemical synthesis techniques to modify these structures, transforming them from "poison" to "medicine". This process requires not only a deep understanding of the mechanism of action of the toxins, but also the mastery of advanced synthetic chemistry and pharmacology techniques.
|
|
|
|
|
The molecular design of Mazdutide: The leap from toxin to therapeutic peptide
The development of Mazdutide began with in-depth research on mammalian gastric acid-regulating hormone (Oxyntomodulin, OXM). OXM is a naturally occurring gastrointestinal hormone secreted by intestinal L cells, possessing the dual characteristics of simultaneously activating GLP-1R and GCGR, and being able to regulate energy balance, glucose metabolism, and weight control. However, the half-life of natural OXM is short, requiring frequent administration, which limits its potential for clinical application.
To overcome this limitation, scientists drew on the design concept of deep-sea toxins and chemically modified the OXM to extend its duration of action. Specifically, they introduced a fatty acyl side chain into the OXM molecule, forming a long-lasting synthetic peptide. This modification strategy significantly prolonged the half-life of the drug, enabling it to be administered once a week, greatly enhancing patient compliance.
More importantly, the molecular design of Mazdutide also incorporates a profound understanding of the structure-activity relationship of toxins. For instance, specific amino acid residues in its sequence (such as AEEA-AEEA-γ-Glu-diacid-C20 linker) may enhance the binding affinity to GLP-1R and GCGR by mimicking the key active sites in the toxin. This design not only retains the dual agonistic effect of OXM but also optimizes the receptor activation ratio, avoiding the side effects (such as elevated blood sugar caused by excessive activation of GCGR) that may result from over-stimulation of a single receptor.
Clinical Validation: The Breakthrough from Laboratory to Patient
The clinical research of Mazdutide peptide has fully verified the feasibility of its design concept. Multiple trials have shown that Mazdutide performs well in lowering blood sugar and reducing weight, with good safety. For instance, in a 2nd-phase clinical study targeting Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes, after 20 weeks of treatment with Mazdutide, the patients' glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels significantly decreased, with the weight reduction reaching up to 7.8% and showing a dose-dependent pattern. Moreover, Mazdutide also improved the patients' blood lipids, blood pressure, and insulin sensitivity, providing a new strategy for the comprehensive management of metabolic syndrome.
|
|
|
|
The achievement of these results is inseparable from the inspiration transformation of the structure of deep-sea toxins. The design of Mazdutide not only demonstrates the precise grasp of the activity of natural molecules, but also showcases the great potential of chemical modification techniques in improving the pharmacokinetic properties of drugs.
Future Outlook: From Metabolic Diseases to Broader Fields
The success of Mazdutide has set a new benchmark for the treatment of metabolic diseases, but its impact goes far beyond this. As the understanding of the dual agonist mechanism of GLP-1R/GCGR deepens, Mazdutide and its analogues are expected to demonstrate therapeutic potential in areas such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and cardiovascular diseases. Moreover, its design concept also provides a reference for the development of other multi-target drugs, promoting the paradigm shift in drug research from "single target" to "network regulation".

From the toxins of deep-sea creatures to the inspiration for therapeutic peptides, the development process of Mazdutide demonstrates the perfect integration of nature and technology. It reminds us that nature holds countless "chemical wisdom" that has yet to be discovered, and the mission of scientists is to transform this wisdom into drugs that benefit humanity through innovative technologies. In the future, as we further explore the complexity of biological molecules, we are likely to witness the birth of more breakthrough drugs like Mazdutide, bringing new hope to human health.

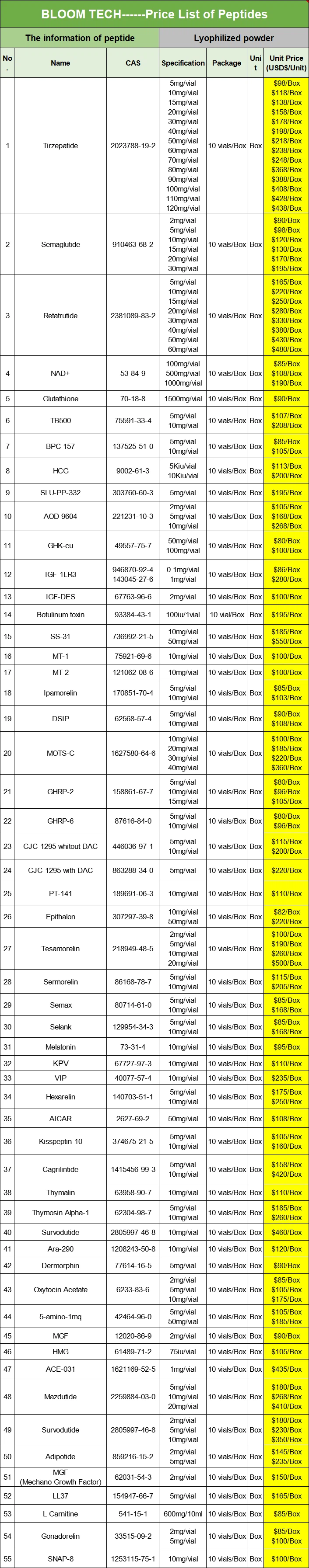
Hot Tags: mazdutide peptide, suppliers, manufacturers, factory, wholesale, buy, price, bulk, for sale, Cosmetic, DERMORPHIN, dermorphin in humans, dermorphin peptide, Melanotan ii powder
















